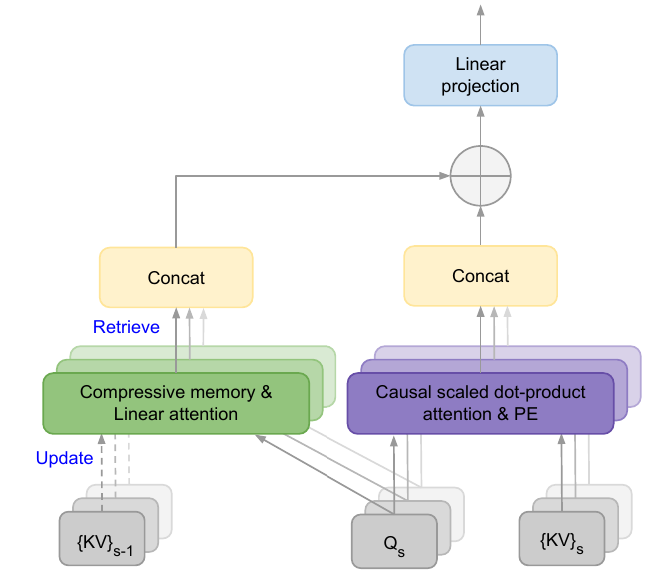
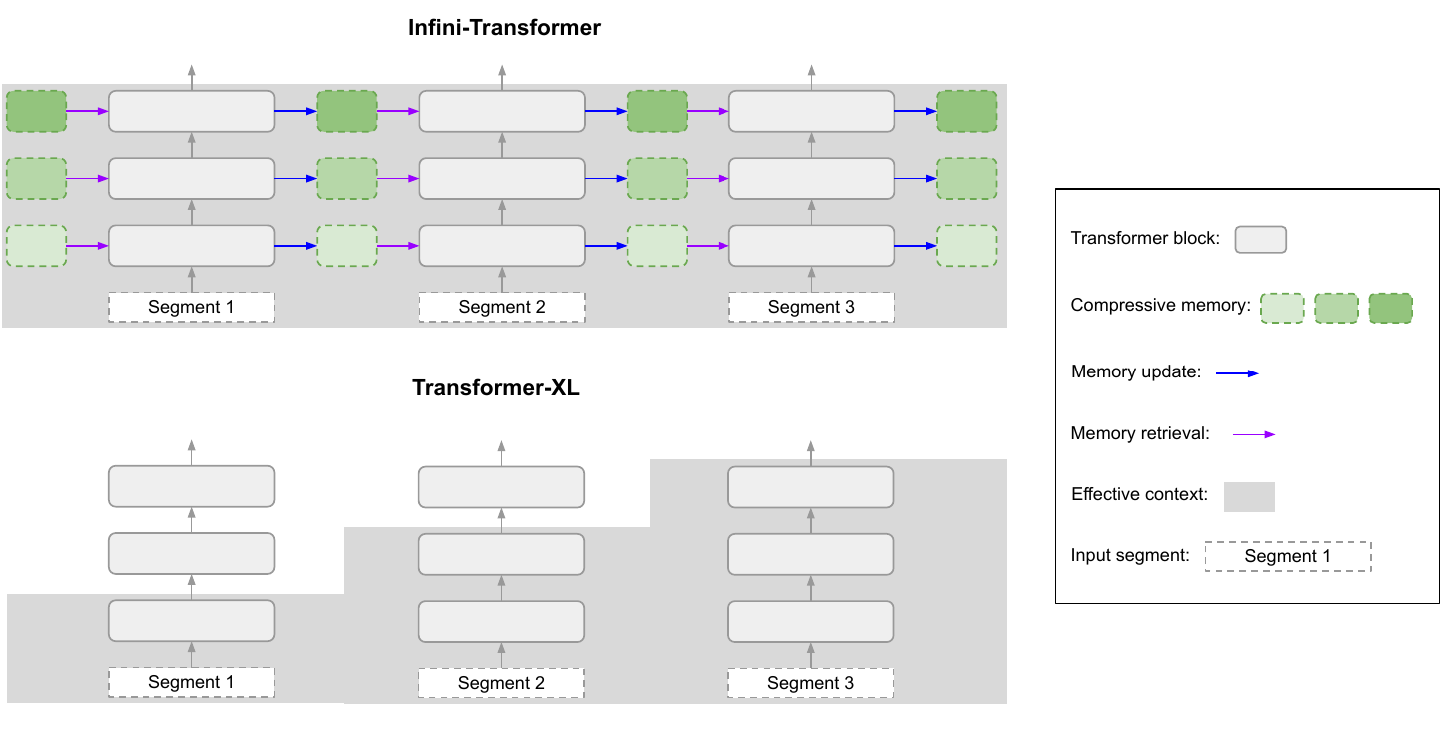
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
| class InfiniAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, seq_len: int, emb_dim: int,
d_head: int, n_head: int, n_segments: int,
is_causal: Optional[bool] = True, update: Optional[str] = 'linear',
use_rope: Optional[bool] = True, device: Optional[str] = 'cpu'):
super().__init__()
"""
Args:
seq_len: Sequence length of the inputs.
n_segments: Number of segments (must be divisible to seq_len).
n_head: Number of attention heads.
emb_dim: Embedding dimension of the input.
d_head: Embedding dimension of each head.
is_causal: Whether the model causal or not.
use_rope: Use Rotary Positional Embeddings or not. Default: True.
device: cuda or cpu.
"""
if update not in ['linear', 'delta']:
raise ValueError('Update takes only one of these parameters - linear, delta')
assert seq_len % n_segments == 0, 'seq_len must be divisible to n_segments'
assert emb_dim % n_head == 0, 'emb_dim must be divisible to n_head'
self.seq_len = seq_len
self.n_segments = n_segments
self.n_head = n_head
self.emb_dim = emb_dim
self.d_head = d_head
self.is_causal = is_causal
self.use_rope = use_rope
self.update = update
self.device = device
self.beta = nn.Parameter(torch.ones((1,), device=device))
self.q = nn.Linear(emb_dim, emb_dim, device=device)
self.k = nn.Linear(emb_dim, emb_dim, device=device)
self.v = nn.Linear(emb_dim, emb_dim, device=device)
self.o = nn.Linear(emb_dim, emb_dim, device=device)
self.elu = nn.ELU()
self.freq_cis = RoPE.compute_freq_cis(emb_dim, seq_len, 10000.0, device=device)
self.register_buffer('causal', torch.tril(torch.ones(seq_len // n_segments, seq_len // n_segments, device=device)))
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
batch_size, _, _ = x.size()
memory = torch.zeros((self.n_head, self.d_head, self.d_head)).to(self.device)
z = torch.zeros((self.n_head, self.d_head, 1)).to(self.device)
query = self.q(x)
key = self.k(x)
value = self.v(x)
if self.use_rope:
query, key = RoPE.RoPE(self.freq_cis, query, key, self.device)
query = query.view(batch_size, self.n_head, self.n_segments, self.seq_len // self.n_segments, self.d_head)
key = key.view(batch_size, self.n_head, self.n_segments, self.seq_len // self.n_segments, self.d_head)
value = value.view(batch_size, self.n_head, self.n_segments, self.seq_len // self.n_segments, self.d_head)
output = []
for idx in range(self.n_segments):
sigma_q = self.elu(query[:, :, idx, :, :]) + 1.0
sigma_k = self.elu(key[:, :, idx, :, :]) + 1.0
A_mem = (sigma_q @ memory) / ((sigma_q @ z) + 1e-6)
A_dot = query[:, :, idx, :, :] @ key[:, :, idx, :, :].transpose(-2, -1)
if self.is_causal:
A_dot.masked_fill_(self.causal == 0, float('-inf'))
A_dot = F.softmax(A_dot / torch.sqrt(torch.tensor(self.d_head)), dim = -1)
A_dot = A_dot @ value[:, :, idx, :, :]
attention = (F.sigmoid(self.beta) * A_mem) + ((1 - F.sigmoid(self.beta)) * A_dot)
if self.update == 'linear':
memory = memory + (sigma_k.transpose(-2, -1) @ value[:, :, idx, :, :])
else:
delta = (sigma_k @ memory) / ((sigma_k @ z) + 1e-6)
memory = memory + (sigma_k.transpose(-2, -1) @ (value[:, :, idx, :, :] - delta))
z = z + sigma_k.sum(dim = -2, keepdim = True)
output.append(attention)
attention = torch.concat(output, dim = 2).view(batch_size, self.seq_len, self.emb_dim)
return self.o(attention)
|