LangChain(二)——Model I/O
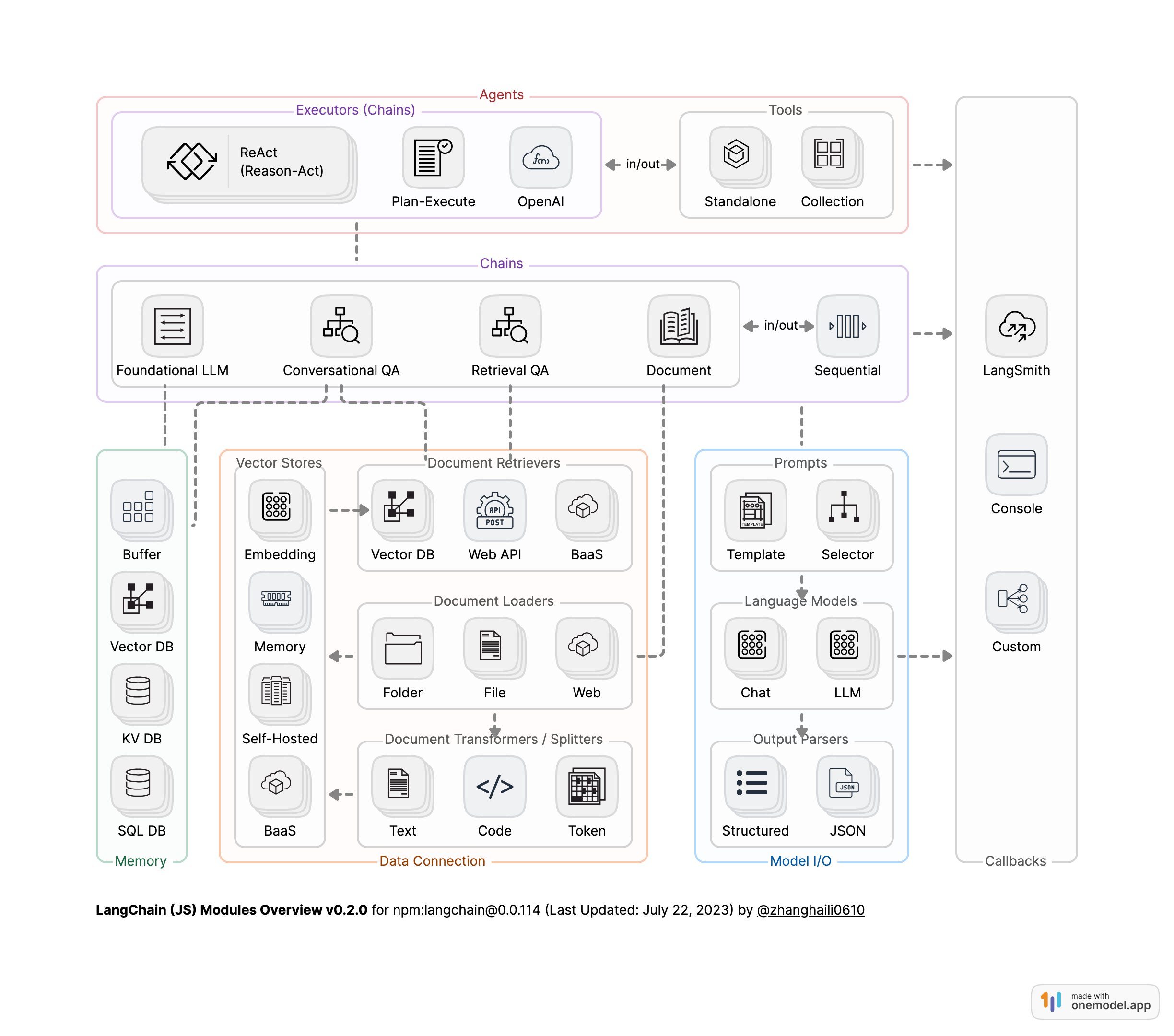
LangChain模块架构图 [1]
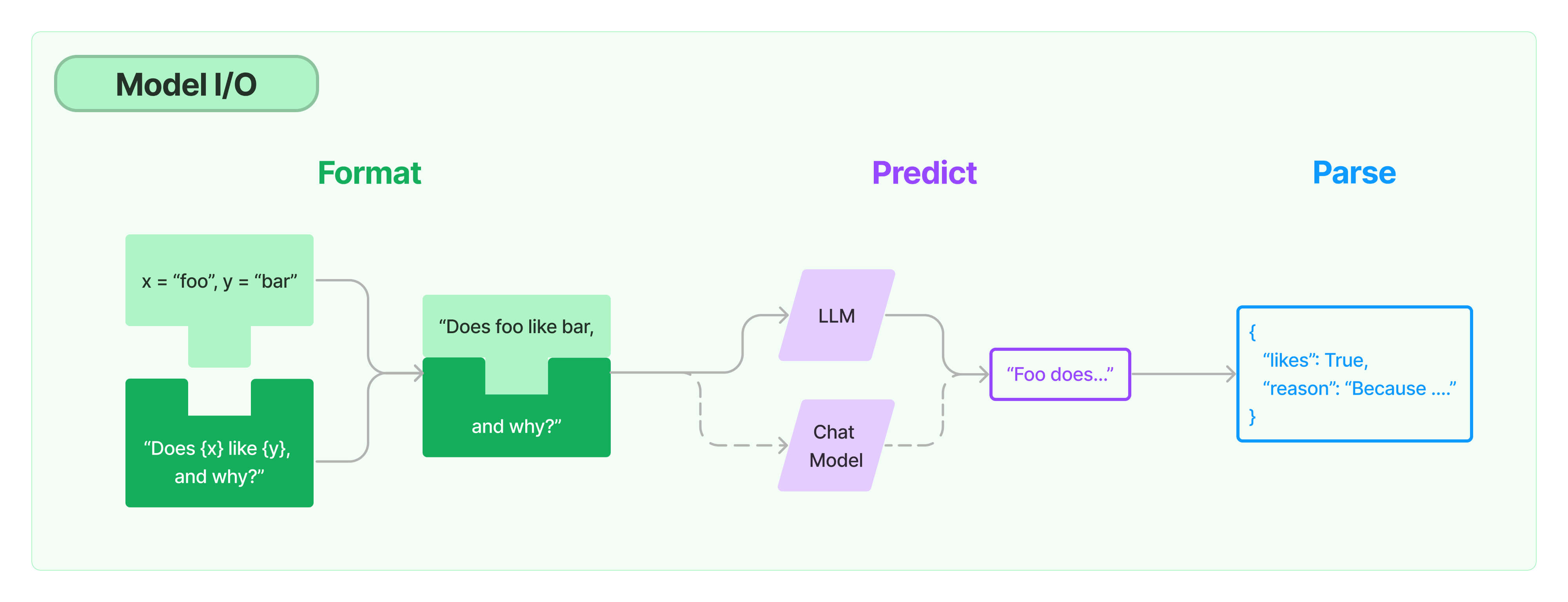
一、Model I/O 简介
Model I/O三元组
- PromptTemple:模板化、动态选择和管理模型输入
- Language Models:通过通用接口调用LLM
- OutputParser:从LLM输出中提取信息
数据流:Prompt->Model->Output Parser
二、模型API
2.1 OpenAI模型封装
1 | |
输出
1 | |
2.2 多轮对话Session封装
2.2.1. 消息组成
- 角色(Role):描述消息的发送者是谁。
- 内容(Content):消息的具体内容,可以是:
- 字符串(大多数模型处理这种类型的内容)
- 列表(包含字典),用于多模态输入,字典中包含输入类型和位置的信息。
- 附加参数(additional_kwargs):用于传递关于消息的额外信息,通常用于特定提供商的输入参数,而非通用参数。一个著名的例子是OpenAI的
function_call。
2.2.2 消息类型
- HumanMessage:代表用户的消息,通常只包含内容。
- AIMessage:代表模型的消息,可能包含
additional_kwargs,例如使用OpenAI工具调用时的tool_calls。 - SystemMessage:代表系统消息,指示模型如何行为,通常只包含内容。并非所有模型都支持这种类型。
- FunctionMessage:代表函数调用的结果。除了
role和content,此消息还有一个name参数,表示产生此结果的函数名称。 - ToolMessage:代表工具调用的结果。与FunctionMessage不同,为了匹配OpenAI的
function和tool消息类型。除了role和content,此消息还有一个tool_call_id参数,表示产生此结果的工具调用的ID。
1 | |
输出
1 | |
2.3 通义千问
1 | |
输出
1 | |
2.4 Tool calling
支持工具调用特性的 LangChain ChatModels 实现了一个
.bind_tools 方法,该方法接收一个 LangChain
工具对象、Pydantic 类或 JSON Schemas
的列表,并以提供商特定的预期格式将它们绑定到聊天模型。
2.4.1 工具实现
LangChain Tool
使用 @tool 装饰器在 Python 函数上定义自定义工具的模式:
1 | |
Pydantic class
也可以等效地使用 Pydantic 来定义模式
1 | |
2.4.2 Tool calling
使用 bind_tools() 方法来处理将 Multiply 转换为“工具”,并将其绑定到模型(即,每次调用模型时都传递它)。
工具调用包含在 LLM 响应中,它们将作为 .tool_calls 属性中的 ToolCall 对象列表附加到相应的 AIMessage 或 AIMessageChunk(流式传输时)。 ToolCall 是一个类型化字典,其中包括工具名称、参数值字典和(可选)标识符。 没有工具调用的消息默认为此属性的空列表。
1 | |
输出
1 | |
输出解析器可以进一步处理输出
1 | |
输出
1 | |
当仅使用bind_tools(tools)时,模型可以选择是否返回一个工具调用、多个工具调用或根本不返回工具调用。
某些模型支持 tool_choice 参数,该参数能够强制模型调用工具。
对于支持此功能的模型,可以传入希望模型始终调用
tool_choice="xyz_tool_name" 的工具名称。 或者您可以传入
tool_choice="any"
来强制模型调用至少一个工具,而无需具体指定哪个工具。
1 | |
2.5 流式响应
当在流式上下文中调用工具时,消息块将通过
.tool_call_chunks 属性使用列表中的工具调用块对象填充。
ToolCallChunk 包含工具名称、参数和 id
的可选字符串字段,并包含可用于将块连接在一起的可选整数字段索引。
由于消息块继承自其父消息类,因此具有工具调用块的
AIMessageChunk 还将包含 .tool_calls 和
.invalid_tool_calls 字段。
这些字段是从消息的工具调用块中解析的。
1 | |
输出
1 | |
添加消息块将合并其相应的工具调用块
1 | |
输出
1 | |
部分解析
1 | |
输出
1 | |
三、Prompt 模板
3.1 Prompt 模板封装
- PromptTemplate 可以在模板中自定义变量
1 | |
输出
1 | |
- ChatPromptTemplate 用模板表示的对话上下文
1 | |
输出
1 | |
- MessagesPlaceholder 把多轮对话变成模板
1 | |
输出
1 | |
3.2 从文件加载 Prompt 模板
1 | |
输出
1 | |
四、输出封装 OutputParser
自动把 LLM 输出的字符串按指定格式加载。
LangChain 内置的 OutputParser 包括:
- ListParser
- DatetimeParser
- EnumParser
- JsonOutputParser
- PydanticParser
- XMLParser
等等 [2]
4.1 Pydantic (JSON) Parser
自动根据 Pydantic 类的定义,生成输出的格式说明
1 | |
1 | |
{“properties”: {“year”: {“title”: “Year”, “description”: “Year”,“type”: “integer”}, “month”: {“title”: “Month”, “description”: “Month”,“type”: “integer”}, “day”: {“title”: “Day”, “description”: “Day”,“type”: “integer”}, “era”: {“title”: “Era”, “description”: “BC or AD”,“type”: “string”}}, “required”: [“year”, “month”, “day”, “era”]}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8====Prompt=====
提取用户输入中的日期。
The output should be formatted as a JSON instance that conforms to the JSON schema below.
As an example, for the schema {"properties": {"foo": {"title": "Foo", "description": "a list of strings", "type": "array", "items": {"type": "string"}}}, "required": ["foo"]}
the object {"foo": ["bar", "baz"]} is a well-formatted instance of the schema. The object {"properties": {"foo": ["bar", "baz"]}} is not well-formatted.
Here is the output schema:1
2
3
4
5
6用户输入:
2077年八月6日,三体舰队打过来了
====模型原始输出=====
{"year": 2077, "month": 8, "day": 6, "era": "AD"}
====Parse后的输出=====
year=2077 month=8 day=6 era='AD'
4.2 Auto-Fixing Parser
利用 LLM 自动根据解析异常修复并重新解析
1 | |
输出
1 | |